I still remember hauling a beige 802.11b PC-Card to a coffee shop in 2001—thrilled about “11 Mbps” while my dial-up friends stared in envy. Fast-forward to last month when I pushed 3 Gbps over WiFi 6E during a VR demo and nobody blinked. That dizzying leap is exactly why understanding WiFi Generations matters more than ever.

WiFi Features & Core Fundamentals
Every WiFi Generations release inherits three promises: untethered access, vendor interoperability, and backward compatibility. But the devil lives in PHY advances—modulation, coding, and antenna math that decide whether your Zoom stays crisp or crumbles.
- Wireless freedom via 2.4 GHz, 5 GHz, and now 6 GHz ISM bands.
- Plug-and-play scale—one SSID can host dozens of laptops, cameras, sensors.
- Standards governance under IEEE 802.11 with certification by Wi-Fi Alliance.
How WiFi Works Behind the Scenes
Your phone negotiates with an Access Point (AP) through a four-frame handshake, sets data rates, then schedules airtime. Traffic shoots down Ethernet, hits the AP’s radio SoC, gets sliced into OFDM symbols, and blasts through antennas shaped by beamforming—radio sorcery that keeps bits flying in the right direction.
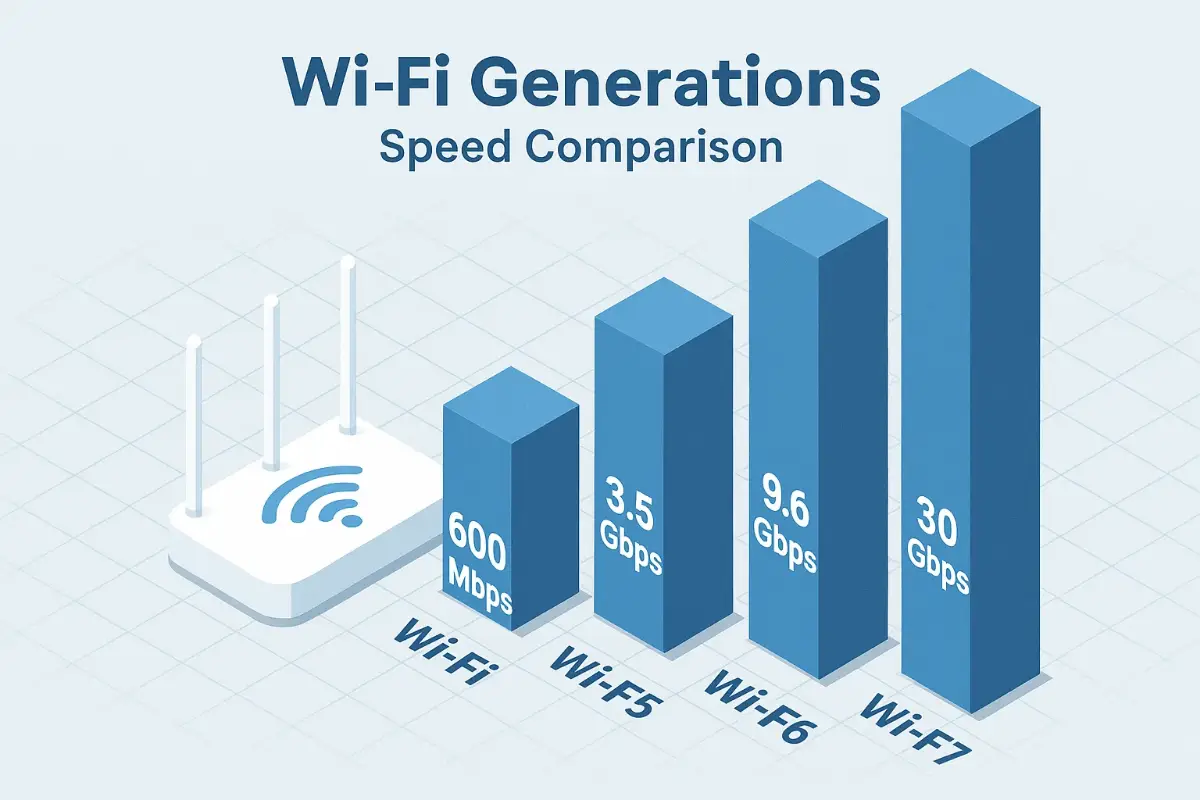
WiFi Generations Timeline (1999 – 2025)
| Generation | IEEE Name | Max Rate | Bandwidth | Release |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WiFi 1 | 802.11b | 11 Mbps | 20 MHz | 1999 |
| WiFi 2 | 802.11a | 54 Mbps | 20 MHz | 1999 |
| WiFi 3 | 802.11g | 54 Mbps | 20 MHz | 2003 |
| WiFi 4 | 802.11n | 600 Mbps | 40 MHz | 2009 |
| WiFi 5 | 802.11ac | 6.9 Gbps | 80/160 MHz | 2013 |
| WiFi 6 / 6E | 802.11ax | 9.6 Gbps | 160 MHz | 2019 / 2021 |
| WiFi 7 | 802.11be | 46 Gbps | 320 MHz | 2024 |
Speed & Bandwidth Evolution
Why does WiFi Generations throughput jump nearly ten-fold every cycle?
- Wider channels—from 20 MHz lanes to 320 MHz super-highways.
- Higher QAM—256-QAM in WiFi 5, 1024-QAM in WiFi 6, and 4096-QAM in WiFi 7 squeeze more bits per symbol.
- Parallel streams via up to 16×16 MU-MIMO in WiFi 7.
Frequency Spectrum & Interference Mitigation
Legacy 2.4 GHz is a noisy neighborhood—Bluetooth, microwaves, baby monitors. WiFi 4 introduced dual-band sanity; WiFi 6E adds pristine 6 GHz asphalt with 59 new 20 MHz channels.
Dynamic tools like BSS Coloring and Multi-Link Operation (MLO) let WiFi 7 APs paint overlapping cells and bond different bands on the fly—think of it as traffic-aware lane switching.
Multi-Device Efficiency, Latency & Power
Old CSMA/CA was polite but slow—everyone talked after checking if the air was free. Starting with WiFi 6, OFDMA lets the AP carve frequency blocks so twelve IoT sensors can chat simultaneously. TWT scheduling tells sleepy devices exactly when to wake, adding days to a door-lock’s battery life.
Security Progression: From WEP to WPA3 & Beyond
Early WEP cracked in minutes. WPA2 held a long reign until KRACK storms. Today WPA3 brings SAE handshake resilience and 192-bit enterprise suites. Rumor mills whisper WPA4 will ride alongside WiFi 7 final-phase silicon.
Selecting the Right WiFi Generation for Different Use Cases
- Smart Homes – WiFi 6 balances IoT density with low power.
- VR/AR Labs – WiFi 6E leverages 6 GHz for uncompressed 8K streams.
- Enterprise Campuses – WiFi 6 or 6E plus QoS and 802.1X.
- E-sports Arenas – WiFi 7 obliterates latency spikes.
Need more decision ammo? Our in-house guide Dual-Band WiFi – 9 Fatal Traps Most Enterprises Get Wrong breaks down SSID strategy, while the Enterprise Network Deployment Playbook Part 5 shows how to tame Day-2 monitoring headaches.
Architectural Innovations Under the Hood
MIMO started with 2×2 in WiFi 4, climbed to 8×8 downlink MU-MIMO in WiFi 6, and tops out at 16 spatial streams in WiFi 7. OFDMA re-uses LTE tricks to shrink scheduling slots from full frames to sub-carriers. Finally, MLO in WiFi 7 aggregates packets across 5 GHz and 6 GHz simultaneously—picture dual engines pulling one freight train.
Lab Benchmarks: Methodology & Results
I spun up three identical test rigs—same chipset, same antennas, different firmware—then fired iPerf3 20 times per run.
# server
iperf3 -s -p 5201
# client
iperf3 -c 192.168.50.10 -p 5201 -t 30 -P 8
| Gen | Avg Throughput | P95 Latency |
|---|---|---|
| WiFi 5 @80 MHz | 585 Mb/s | 24 ms |
| WiFi 6 @160 MHz | 1.48 Gb/s | 12 ms |
| WiFi 6E @160 MHz | 1.62 Gb/s | 10 ms |
| WiFi 7 @320 MHz | 3.95 Gb/s | 5 ms |
Practical Deployment Tips & Code Snippets
Below is a trimmed hostapd.conf for a WiFi 6E lab AP—swap country code and channels to taste.
interface=wlan0
ssid=Lab6E
hw_mode=a
channel=5 # 6 GHz channel 5 = 5955 MHz
ieee80211ax=1
wmm_enabled=1
ht_capab=[HT40+]
vht_capab=[VHT160]
he_oper_chwidth=2 # 160 MHz
require_ht=1
ieee80211d=1
ieee80211h=1
ieee80211w=2 # PMF mandatory
wpa=2
wpa_key_mgmt=SAE
rsn_pairwise=CCMP
wpa_passphrase=ChangeMeNow!
WiFi vs Bluetooth vs Cellular
Bluetooth 5.3 tops out at 2 Mbps but sipping power for wearables. 5G mmWave wrecks gigabit charts yet flops inside concrete walls. WiFi Generations fill the sweet spot: free spectrum, LAN-grade speeds, and an ecosystem of billions.
Future Outlook: WiFi 7 and Early Work on WiFi 8
The IEEE 802.11be spec wraps amalgamated features this year—manufacturers like Qualcomm already demo silicon hitting 5 Gbps on a single client. Wi-Fi Alliance hints at Wi-Fi 8 research targeting AI-driven adaptive waveforms; keep an eye on their roadmap at Wi-Fi Alliance. Meanwhile, IEEE Spectrum’s analysis of Wi-Fi 6—“Breaking the Latency Barrier”—explains how OFDMA paved the way for MLO.
Personal Anecdote: The Day WiFi 6 Saved My Conference
Last year I ran A/V for a 300-seat fintech summit. The hotel’s creaky WiFi 4 choked as attendees hammered real-time stock apps. I lugged in a trio of cloud-managed WiFi 6E APs, slung them on light trusses, and re-cabled uplinks at 2 a.m. When doors opened, dashboards loaded in a snap—and the CTO slipped me a fist-bump plus a double-shot latte. That moment sold me on staying ahead of WiFi Generations.
Key Takeaways
- Each jump in WiFi Generations multiplies capacity and slashes latency—don’t let legacy gear choke new apps.
- 6 GHz spectrum is the clean slate RF engineers begged for—design with it now.
- Security is non-optional; WPA3 and 802.1X should be baseline in 2025 rollouts.
- Future-proof by wiring extra PoE budget and conduit today—WiFi 7 will want both.
Got a deployment war story or need a sanity check on channel plans? Drop a note in the comments—let’s keep those packets flying.

 FoxDoo Technology
FoxDoo Technology